
|
Being one of the oldest areas of social activity, medicine has gone through a long way of development, accumulating and generalizing practical experience, and employing achievements of scientific and social studies. Each stage in the development of medicine is marked by new achievements in the areas of theoretical thought, clinical observations and practical skills and expanding available means of diagnostics, prevention and treating of diseases. In Ancient Russia treating was conducted by quacks and magi. Some of the oldest written sources prove that there was a certain specialization of quacks - professionals, who have empirically mastered certain ways of treating: "blood-letting" (in Ancient Novgorod they formed unions similar to medieval trade guilds). Since the acceptance of Christianity a new type of quacks has emerged - a monk-quack. There were also secular physicians, providing services to armies of different princes, and physicians in the rank of trade people. In 1581, by decree of Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible), the Pharmacy Department was formed - the highest authority in governing medicine in Moscow State of 16-17 centuries. The Pharmacy Department was staffed by physicians, quacks, pharmacists, pharmaceutical technicians and their assistants, barbers, surgeons, eye-doctors, alchemists and others. One of its functions was preparing native medical cadre: physicians, surgeons and pharmacists. Social, economical and political development of Russia in 18-19 centuries, emergence of regular army and navy required creation of the organized system of medical service and emphasized the need to train treating physicians and other medical specialists. To meet this need certain steps were undertaken in organizing the system of Russian medical education, first of all by the way of creating medical schools at large, so called general, military hospitals. In 1707 the Moscow General Army Hospital (now - the Main Clinical Military Hospital named after N.N. Burdenko) was opened, created by the decree of Peter the Great, along with medical school aimed at preparing physicians for this hospital. In 1733 three more hospital schools were opened in St. Petersburg and Kronshtadt. In 1786 hospital schools were separated from hospitals and transformed into medico-surgical academies. In 1757 first midwife schools were opened. Starting in 1829 the process of creating schools with a 4-year curriculum at large hospitals has begun. The Structure of the Health Care System in Russian FederationIn the Russian Federation the combination of three systems of Health Care - state, municipal and private - is preserved. The State System is comprised of the following: Factories, institutions and organizations of the State Health Care system, regardless of their departmental subordination are considered to be legal entities. They conduct their activity in accordance with "The Basic Laws on the Protection of Citizens Health" of the Russian Federation (further - "Basic Laws") and other corresponding legal acts and laws of the Russian Federation and its subjects, as well as directives of the Ministry of Health Care of the Russian Federation and Ministries of Health Care of the subjects of the Russian Federation and by local administrations. The Municipal System of Health Care is comprised of
the following: Institutions of municipal Health Care system are considered to be legal entities. They conduct their activity in accordance with "Basic Laws" and other legal acts of the Russian Federation and the Russian Federation subjects, legal acts of autonomous regions, areas and cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg, legal acts of local administrations. Self-governing municipal authorities in charge of Health Care are responsible for sanitary and hygienic education of people, for providing people with an access to a guaranteed level of medical and sanitary services, for the development of Municipal Health Care system, for the quality control of medical, social and pharmaceutical services provided by all institutions located on the territory of municipality. Financing of institutions, companies and organizations of the Municipal Health Care system is conducted from the budgets of all levels, specialized funds created for supporting public health and from other sources allowed by the laws of the Russian Federation. The Private System of Health Care is comprised of: Privately owned treating and prophylactic institutions, as well as people engaged in private medical practice and in private pharmaceutical practice. The system also includes treating and prophylactic institutions, pharmaceutical, scientific, research and educational institutions, created and financed by private companies, institutions and organizations, public organizations and individuals. The institutions of this system conduct their activities in accordance with "Basic Laws" and other legal acts of the Russian Federation and the Russian Federation subjects, legal acts of local administrations, as well as legal acts of the Ministry of Health Care of the Russian Federation and of local authorities. Licensing of Medical InstitutionsMedical institutions of all types of ownership are required to have a license for a certain type of activity to conduct this activity. License may be issued on the basis of certificate demonstrating that conditions of this activity correspond to the standards set for each type of activity by licensing commissions of the state authorities of the Russian Federation subjects. Medical institutions have to submit to the licensing commission a set of 11 documents. Licensing procedure includes reviewing of documents submitted by the institution, conducting local expertise and issuing a license to provide medical services in a requested scope, or with some limitations, or a grounded refusal to issue a license. Commission determines the time period during which the license remains valid - not more than 5 years for state institutions and not more than 3 years for institutions with non-state forms of ownership. In a case when license is suspended or annulled its owner shall be notified in no later than 10-day period since the decision was made. In 10 days after notification of the annulment of the license, the owner shall return it to the authority, by whom the license was issued. In a case of a dispute between an institution and a licensing commission, each party may apply to a licensing commission of the republic in a period of 15 days since notification of the decision of the local licensing commission. In a case when a dispute is resolved in favor of the applicant, the latter has a right to file a claim with a court to reimburse his losses. Accreditation of Medical InstitutionsAll medical institutions, regardless of the type of ownership, as well as people engaged in providing, individually or collectively, services in medical insurance are subject to accreditation, i.e. verifying compliance to the set professional standards. The order of submitting documents in a corresponding accreditation commission and their review is similar to procedure of obtaining a license. Based on the submitted documents, the accreditation commission may issue a certificate, acknowledging the compliance of the claimed types of medical services to the set standards, or to refuse to issue a certificate. Quality Control of Medical ServicesThe Ministry of Health Care of the Russian Federation and Federal Fund of Compulsory Medical Insurance have issued a joint order dated September 24, 1996 m 363/7 "On improving the quality control of medical services provided to the population of the Russian Federation", by which the system of quality control was established. There are two types of quality control of medical services - departmental and non-departmental control. In accordance with "Basic Laws" and such Laws as "On medical insurance in the Russian Federation", "On customers rights protection" and other legal acts, the goal of departmental control is to assure rights of patients to receive medical services of the required scope and quality. The system of non-departmental control has a similar legal
basis. The goal of this system is to assure rights of people for health
protection. The control is implemented by: In order to assure cooperation between departmental and non-departmental quality control of medical services, the subjects of the latter may file an inquiry with the clinical expert commission of Treating and Prophylactic institution (TPI) or corresponding health care administration about the results of the departmental control, review them and, if agreed, make corresponding decisions and implement necessary measures without conducting additional expertise. Sources of Financing of Health Care SystemThe financing of Health Care System in a situation of
medical insurance is provided by means of: From all the financial sources for Health Care the budgets of state and municipal health care systems are formed as well as budget of the state system of Compulsory Medical Insurance (CMI). The financing of the TPI is provided by means of: Taxation of Paid Medical Services Paid medical services are considered to be entrepreneurial activity of medical institution, and that is why the institution has to pay the following taxes: 1. Tax on the users of automobile roads. At the rate of 2.5% of income. The collected funds are transferred to: Federal Road Fund of Russian Federation at the rate of 1.25%, Local Road Fund at the rate of 1.25%. 2. Special taxation of individuals, companies, organizations and institutions directed for support of militia, improvements of territories, needs of education system and other goals. The maximum tax is determined by the Law of the Russian Federation dated July 16, 1992 m 3317-1 and may not exceed per year 3% of 12 minimal monthly salaries determined by law for individuals, for all types of special taxation total. Local administration by its decisions may provide relief of local taxes in accordance with article 10 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On the basis of Tax System of the Russian Federation". If there is no income from entrepreneurial activities, budget organizations may be relieved from special taxation. 3. Tax for support of Housing Fund and institutions of social and cultural areas, at the rate of not more than 1.5% of the volume of realized production, manufactured by legal entities, located on the corresponding territory. 4. Tax for the needs of educational facilities. The tax shall not exceed 1% of the annual fund of salaries of companies, institutions, and organizations located in republics of the Russian Federation. The relief from paying this tax may be provided to budget institutions if they are not involved in entrepreneurial activities. 5. In accordance with instruction of State Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 11, 1995 m 39 and Letter of State Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 20, 1997 m B3-6-18/743, the following entities, regardless of the source and form of payment, may be relieved from Tax on Added Cost: paid medical services for population; drugs, among them medical substances including those of in-pharmacy preparation, other medical products, prosthetic and orthopedic products and medical equipment, as well as manufacturing and repair of eye-ware (lenses and frames for glasses, except for sunglasses); repair of hearing-aid equipment, prosthetic and orthopedic products. Tax relief is not offered for veterinary as well as sanitary and epidemiological services. 6. Organizations who, by legal acts of State Legal Authorities of the Russian Federation subjects, are transferred to an unilateral tax on temporary income in accordance with the Federal Law dated July 31, 1998 m 148-F3. The unilateral tax has to be paid by organizations engaged in entrepreneurial activity in the area of providing medical and cosmetology services. According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 15, 1996 m 478, the income from realization of vitally necessary and most important medicines and other medical products received by companies of all organizational and legal types who have produced these medicines and other medical products, is not subject to taxation. In the first two years of their work, small companies, producing and at the same time reprocessing medical equipment, medicines and other medical products, do not have to pay income tax. *The transport tax in not being withdrawn according to the Decree of President of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 1997 m 1233, which has canceled the Decree of President of the Russian Federation dated December 22, 1993 m 2270. Medical Insurance in the Russian FederationPrior to 1919 medical insurance in Russia reflected, in
general, European tendencies, but also had some unique features predetermined
by the peculiarities of the Russian History. In the development of medical
insurance as a whole the following periods may be outlined: Starting in 1993, two types of medical insurance coexist in Russia: Compulsory in Voluntary. Compulsory medical insurance (CMI) is part of the system of social insurance. In Russia, social insurance is viewed as a system, guaranteed by the State, and aimed at providing material well-being of people in old age or in an event of sickness or disability, support of motherhood and young children, and healthcare. Financing for social insurance is provided by means of payments by companies, institutions and organizations of all types of ownership, and payments by people, engaged in private business. The scope and order of payments are determined by law. Prior to 1991 payments by most companies were done at the rate of 26% of salary fund, later they were increased. At present, the Law of the Russian Federation "On the rates of payments to the fund of social insurance of the Russian Federation, to the state fund of employment of population of the Russian Federation and to the funds of compulsory medical insurance" sets the payment to the fund of compulsory medical insurance at the rate of 3.6% (3.4% go to the Local Fund, 0.2% - to the Federal Fund) in relation to the salary fund and less than 10% of all funds of social insurance. Public organizations of handicapped people and other public institutions are relieved from payments. Diagram of moving the financial resources in the system
of CMI of the Russian Federation. As shown in the following diagram, major ways through which finances are transferred in the system of CMI in Russia, may be divided into 4 groups, reflecting the order and nature of financial cooperation between subjects of medical insurance. The first way (I) is characterized by the order of transferring funds to the Federal and Local funds of CMI from insurers in the face of employers, who are paying insurance payments for their employees at the rate of 3.6% of salary fund, and from local administrations - insurers of unemployed people. The rate of insurance payment for CMI for unemployed people is determined each year by the order of Governor or by the head of local administration. The second way (II) reflects the main directions of spending financial funds at the local funds of CMI. The third way (III) shows the transferring of CMI financial funds to medical insurance organizations and their spending. The fourth way (IV) reflects the transferring of CMI funds to treating and prophylactic institutions and their spending. Voluntary medical Insurance (VMI) was developing as a part of private commercial insurance and shares with it common history. In 1835 private insurance has started in Russia, and Private Insurance Corporation "Life" has been created, which had a monopoly on private insurance till 1847. At present VMI is characterized by a variety of different programs, in which, at the customer's request, such elements may be included as prophylactic insurance, the insurance for the period of rehabilitation, insurance in the event of permanent or temporary disability, life insurance.
Characteristics of Compulsory and Voluntary Medical Insurance
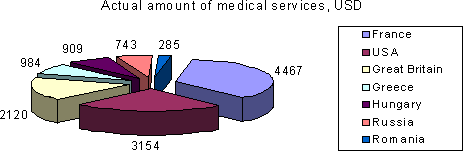
Expenses on Health Care per one inhabitant in 1996
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|

| HEALTH CARE |
This website has been discontinued since 2008.